As critical conveying equipment in grain and oil industries, the proper operation of engineering chain directly impacts production efficiency and safety. However, in actual operation, chain runout in En-Masse Conveyors is a frequent occurrence, leading to equipment malfunction, production interruptions, and even potential safety hazards. This article provides in-depth analysis of engineering chain runout causes in en-masse conveyors and proposes corresponding solutions to enhance equipment reliability and productivity.
Currently, en-masse conveyors are widely used in the grain and oil industry as well as other sectors, serving as critical equipment in material handling and transfer systems. As the core component of an en-masse conveyor, the chain’s operational stability and alignment accuracy directly determine the conveyor’s normal operation and service life, thereby impacting the entire system’s functionality and longevity. However, due to the complexity of working environments, long-term equipment wear, or improper installation/adjustment, chain runout occurs frequently. This article will investigate the root causes of chain runout and propose countermeasures, supported by objective case studies and mechanical principles.
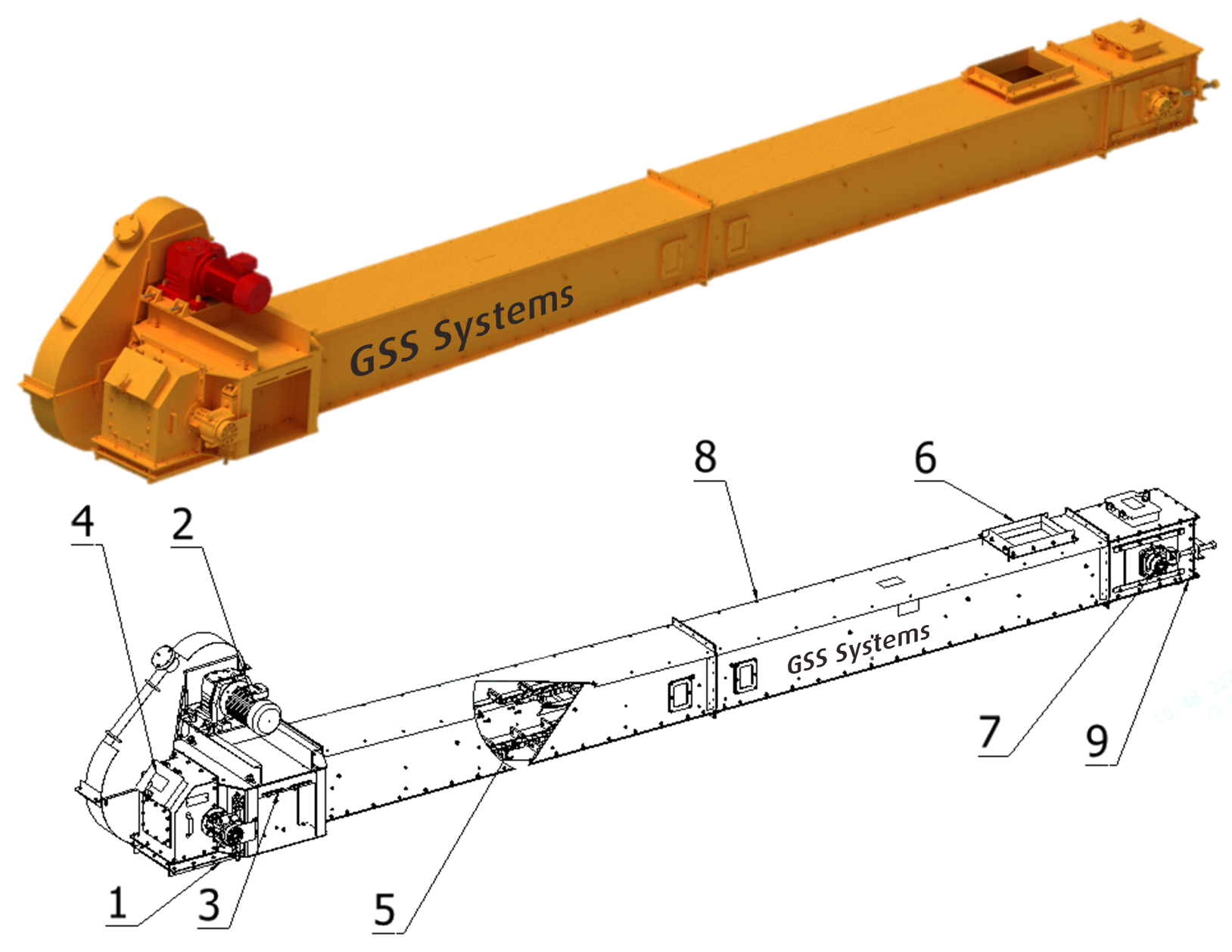
1.1 En-masse conveyor structure
As shown in Figure 1, the en-masse conveyor consists of: head unit, intermediate sections (trunking), tail unit, engineering chain with attachments, monitoring devices, drive system, safety mechanisms, and auxiliary components. The engineering chain and chain attachments are connected to run in the closed body to form a closed and continuous transportation system.
1. Anti-blocking sensor; 2. Powertrain; 3. Chain breakage sensor; 4. Headstock;
5. Engineering chain and chain attachment; 6. Feed inlet; 7. Zero-speed sensor; 8. Intermediate section; 9. Conveyor tail
1.2 Working principle
Material conveyance is achieved via engineering chains that drive connected wear pads and other attachments. When the driving device provides power, the engineering chain runs smoothly on the base plate and rail, and drives the wear pad to push the material forward at the corresponding speed, thus realizing the transportation of the material.
Post Time: 2025-09-04